Gallbladder Surgery
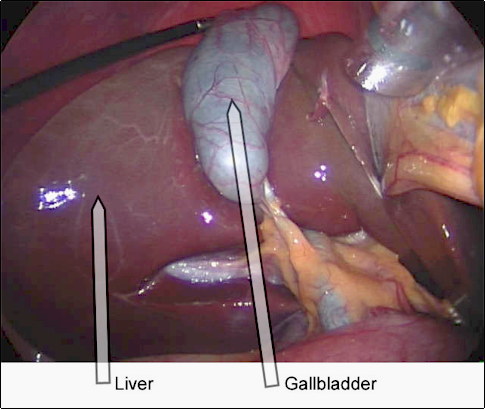
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ located just under the liver and behind the bottom right rib. Gall (bile) is a greenish-brown liquid which the liver produces. Gall is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. Gall goes into the small intestine via the bile ducts to facilitate the digestion, mainly of fats. Every time we eat some gall is released into the intestines. The bile duct is a narrow tube. Bile, a substance produced by the liver, is stored in the gallbladder for release into the gut to help digest fat. When you eat fatty foods, the bile becomes saturated with cholesterol, one of the components of bile. Eventually, the excess cholesterol separates from the bile and begins to calcify, forming stones.

When bile encounters a closed sphincter, it travels back up the duct and veers off towards the cystic duct and into the gallbladder sac. Here in the gallbladder, 90% of the water is removed from the bile. This makes the bile more potent and efficient at performing its functions. The gallbladder, besides concentrating bile, also works with the sphincter of Oddi to start and stop the flow of bile so that it is secreted at optimal times and in optimal amounts. With the removal of the gallbladder that control is removed and left to the sphincter alone.
When we ask about gallbladder function we are really asking about biliary function, or the purpose of bile. It is the bile that performs the tasks we need done; the gallbladder concentrates and regulates the flow of bile. Whether we have an intact gallbladder or have had it removed, we still have the same need of bile.
more about the gallbladder...

The bile has two major functions in the body. Firstly, it breaks down the fats that you eat so that your body can utilize them. Without adequate bile you do not metabolize your fats well which can result in a deficiency of the fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K). You may also have problems digesting the essential fatty acids which are needed for brain development, brain function, eyes, hormones, cholesterol and more. Amongst other symptoms you could have trouble utilizing calcium, have dry skin, peeling on the soles of your feet, etc. One way you can tell you have trouble digesting fats is if you have excessive burping that starts shortly after eating a fatty meal. You might feel nauseous or experience gas and bloating. Often the bile is thick and you can thin it out with diet.
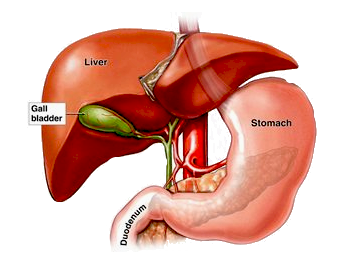
Secondly, bile is a very powerful antioxidant which helps to remove toxins from the liver. The liver filters toxins (bacteria, viruses, drugs or other foreign substances the body doesn't want) and sends them out via the bile, which is made in the liver. The pathway of departure is from the liver through the bile ducts and into the gallbladder or directly into the small intestine where it joins waste matter and leaves through the colon with the feces.



